Note: This is a guest post written by Matthew Denos
“Dad, is my car ready yet?”
“Almost done son. I downloaded the database from Lego.com, changed the color to white, increased the width of the tires, and am now printing out for you to play.”
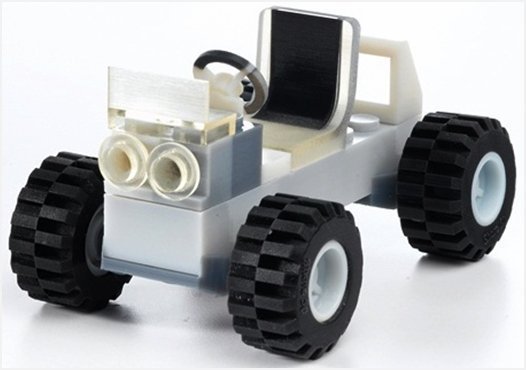
This type of conversation will soon be a reality. The concept of additive manufacturing is taking new shape as it relates to 3D printers. This technology is more than 30-years-old, but is now gaining traction to explore areas that were once unthinkable.
With changes in pricing structure, software and size, just about anyone may have access to a 3D printer in the near future. In fact, this exciting new printing approach already has an impact on various industries such as health, fashion, engineering and architecture, just to name a few. Admittedly, even the everyday DIY person has access to it. Sounds hard to believe? Just search Google for “3D printer” and you will see many companies advertizing their inexpensive 3D printers.
The manufacturing concept this emerging technology uses may be simple, but the potential of 3D printing is by far the next revolution worth watching closely.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing uses the layer manufacturing technique to fabricate products. Once the printer receives the geometric representation of the product, it slices the data into 2-D layers (cross sections). It then builds layer-by-layer using the material that is installed. The bonding process of each layer can either be melting and depositing or deposing and melting.
Material that is in liquid form or powder form can be used to make the final product. When the layer-by-layer process is complete, the product can be removed and used immediately. It can be a final functional piece or form part of another product.
How Does it Differ from 2D printing?
Unlike regular printers that are used to print documents and brochures, a 3D printer turns 3D CAD designs into functional objects. LEGO, children’s famous toy company uses 3D printers to produce the popular plastic building bricks. This is by far the biggest difference that this technology has with 2-D printing—the conventional type of printing that cannot create a functional product.
Who’s using 3D printing?
Just about anyone that has 3D data and knows how to configure a 3D printer to read it can use this technology. Product designers, architects and health care professionals are the main users. But car manufactures and fashion enthusiasts and also joining the trend.
Some major players are using 3D printing to allow customers to interact with the product they are going to buy. This allows the potential client to customize the product according to personal preferences.
The technology can be used to fabricate just about any imaginable product. Both static and functional customization products can be produced. Whether prosthetics for an amputee or a simple pen, all these are just some of the possibilities.
There is current research being conducted about the possibility of using layered cells to build biological organs. To accomplish this, it will be necessary to use organic material and not metal or any other synthetic material. This possibility is still being studied, but there are many fine details to iron out first before it is accepted.
How much does a 3D printer cost?
In the past, 3D printers were only accessible to a selected few given the cost, size and complex operational procedure. Now, it is possible to get a 3D printer for as little as USD$300.
What are the benefits of 3D printing?
[1] Incredible Detail
The technology is able to elaborate intricate details that traditional manufacturing processes are unable to produce. It addition to this, it eliminates the need to use manual labor for certain details. This means faster turnaround time and less expense during the manufacturing stage. The ability to produce fine precision, high-performance parts is a result of its high-resolution feature. A 3D printer has a 4 micron resolution that is truly amazing.

[2] Better implants
The high-resolution feature of 3D printing allows this technology to produce the finest details of any product—even a human jaw! The first transplant jaw made by 3D printing was fitted to an 83-year-old woman’s face in June 2011. The jaw was fabricated using the layering process. The material used was titanium powder and despite the slightly heavier weight than that of a normal jaw, the patient was able to speak right after the surgery and go home within a few days later! This successful operation opens to door to a new era of 3D-printed patient-specific parts.
[3] Speed
A 3D printer works at an incredibly fast pace. You only need to design the product and feed the printer with the necessary data. The artificial jaw mentioned earlier took only a few hours to print once designed.
[4] Less Material
Material waste is eliminated with a 3D printer. This is due to the layering process that creates an exact copy of the geometric CAD figure it must create.
[5] Personal Household Use
You can use 3D printing for you personal, home needs. Products that are discontinued, but can be found on a database of 3D representations can be re-produced. This includes anything from car parts to typical home equipment such as a vacuum cleaner. When you access the information and pass it to the 3D printer you can have a part for any of these in no time.
In fact, today you can download the 3D designs of many home and office products from the web (i.e pencils, cookware, etc). You can also create your own products. You can download from the web parts for specific machines.

Imagine you have a vacuum cleaner in your home, which is broken down. You need to replace a part in order to fix it. You go online and you notice the company has discontinued the product. What do you do? Well, you just find the database of 3D designs that corresponds to the parts of the particular model of your vacuum cleaner. You download this information and you print it. You then use it to replace the broken part of your vacuum cleaner! Many companies and manufacturers are using this technology already.
[6] Mass production
With its ability to produce intricate details at super fast speed, mass production is another benefit of this product. This eliminates the need to send products across the world, since with just a few clicks and a stable internet connection you can basically fabricate any product you imagine. No more sending your design to China to have it mass produced.
[7] Customization
Users can customize products according to their specific needs and preferences. This concept is being adopted my leading brands that are allowing clients to provide the opinions about what they want and like. Instead of visualizing a product that doesn’t exist, you can create your own or tweak a design to fit your specifications. That jewelry that looks like what you have in mind but is not exactly what you want, you can tweak the manufacturer’s design to create what exactly you desire.
[8] Lighter products
Lighter products are produced due to the fact that less material is used during the manufacturing process.
3D printing hurdles to overcome
Despite being around for 30-years not everyone knows how to use a 3D printer. Standards and concepts about 3D layout will have to be established to ensure that the technology is available to the general public. They will also need to fully understand the types of materials that can be used to guarantee functional products.
Source: Objet Ltd press release on 3D Printing technology
Note: This guest post was written by Matthew Denos. He is fascinated by the technological advancements in the world of printing. He provides a Vista Print 50% off coupon and a 123Print.com coupon code in his blog, where he reviews Vistaprint and 123Print—two popular 2D custom printing online destinations known for printing Business Cards, Stationery, Checks, Brochures, Postcards, Magnets, Address Labels, and more.






Comments are closed.