Note: This is a guest post written by Jeeva Shanmugam – Google, the maker of Android, has just released the Developer Preview 1 for Android 14. The launch is timed to go along with prior Android releases. The developer preview 1 includes several user- and backend-facing enhancements.
It’s extremely doubtful that it will undergo a significant makeover like Android 12, but it still appears to be on track to bring about several quality-of-life enhancements including increased battery life, improved UI, and greater accessibility.
Given that Android runs billions of devices globally, people are naturally excited about Android 14 and what it brings. If you’re interested in learning more about Android 14, here are all the necessary details you should be aware of.
Android 14 Developer Preview 1 – A lot more than expected

Android 14 Code Name
Google has a habit of giving the codenames for its Android versions mouthwatering desserts. This is also true with Android 14. The company’s fascinating moniker for the most recent Android is Upside Down Cake. Although codenames are no longer frequently used, Google has naturally kept up the tradition of utilizing fascinating characters in its Android releases.
Android 14 Release Timeline
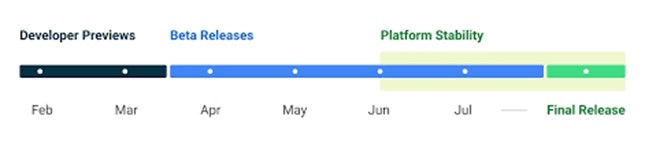
The timeline for Android 14’s releases is the same as it was for preceding Android versions. According to the schedule provided by Google below, there will be two developer previews, the first of which will be released in February and the second in March. Google will presumably release the initial beta sometime in April, but the official release won’t likely happen until later, maybe in May.
Android 14 Supported Devices
According to Google, which mobile devices are compatible with the first developer preview?
As usual, only the Google Pixel phone line qualifies for the developer preview. Later, like with other Android iterations, additional devices from various manufacturers might join the beta program. For devices produced by Xiaomi, Asus, OnePlus, Oppo, Realme, and other Android smartphone manufacturers, beta builds were previously available.
When the beta testing is through, Android 14 is expected to be made available on all existing Android phones, including the flagship models from the last several years. However, depending on your manufacturer, the deployment might take more than a few months. Samsung’s phones frequently get an upgrade within a few months after the stable release; however, this can’t be assured for products produced by Nokia, Infinix, Asus, Motorola, and other lesser-known companies.
Meanwhile, you may install generic system images (GSIs) on any phone that supports Project Treble when Google releases them, which is very guaranteed to happen. Before you consider taking it that way, make sure you are well familiar with how to install an Android beta.
Android 14 Release Date
Platform stability will be attained by the third beta of Android 14, which will be made available in June. As a consequence, while building their apps with the new capabilities and APIs featured in Android 14, app developers won’t need to make any further changes after that. The Android 14 follows the same processes as its predecessors, so if history is any indication, I believe it will be released in August or September.
Android 14 Developer Preview 1: Exclusive Features
Battery Optimization in Android 14

Even though Android standby battery life has considerably increased over time, there is still work to be done. Since Google is making modifications to limit front services to the highest priority user-facing activities alone in Android 14, apps won’t be able to access your phone’s full capacity when they merely need to perform anything in the background. Google is also making it easier for developers to design more intricate background processes, such as limiting an app’s ability to download huge files unless Wi-Fi is available.
Both app developers and users will benefit from an improvement in app optimization as a result. Tighter alarm settings, which stop programs from uninvitedly activating meaningless warnings, are another power-side enhancement.
Commitments to Tablets and Foldable Smartphones
Google is still committed to helping tablets and versatile form factors. The most recent Android release will carry on the initiative to provide a consistent experience across all screen sizes and form factors, which was initially initiated in Android 12L and 13. To help developers create apps that adjust to different screen sizes, Google is creating new components including window size classes, activity embedding, sliding pane layout, and more. All of these will be supported by Jetpack Compose.
Fast Pair and Guest Mode on Android 14
There are many more changes in Android 14 Developer Preview 1 that Google hasn’t yet revealed and hasn’t even touched upon. One of them is the inclusion of a toggle that enables you to enable or disable fast pairs. If you are unfamiliar, fast pair is a relatively new Google feature that enables you to rapidly pair new Bluetooth devices with your phone.
Security Improvements on Android 14
Previous accidental source code leaks showed that Google is restricting sideloading with Android 14. Applications that were released in 2015 with Android 6 and target an SDK version of less than 23 would by default not be able to be installed.
Google notes that malware usually targets older versions of the Android operating system in order to get past restrictions found in SDK versions 23 and higher. Malicious actors will have a lot harder time infecting devices even if they are successful in persuading consumers to sideload an app rather than download it from the Play Store.
Wrapping it All
We must wait till the official debut of Android 14 because they are only the beginning of the changes and additions that are anticipated. We now know a few more things about the upcoming Android version in addition to what Google told us about the developer preview.
That’s because Android is fundamentally an open-source project, and Google must change some of the core code to incorporate new features in the future. Google also revealed a few traits ahead in other circumstances. There have also been several leaks from other sources. What I have found thus far after cleaning it up is as follows.