Note: This is a guest post written by Jeeva Shanmugam – Battery life has become one of the most important issues for consumers as our reliance on smartphones in everyday life grows. We don’t want our phone battery to run out in the middle of the day, especially when we most need it.
Manufacturers have developed fast charging technology that can recharge a phone’s battery in a small fraction of the time required by conventional charging techniques in an effort to address this problem. Fast charging raises the question of whether it might harm your smartphone battery over time. Let’s Find out!
Does Fast Charge Harm Your Smartphone’s Battery?

First and foremost, it’s crucial to comprehend how quick charging functions. A greater voltage is applied to the battery during fast charging to hasten the charging process. Fast charging may give up to 20 volts of electricity instead of the conventional 5 volts, resulting in a much shorter charge time. Qualcomm’s Quick Charge, OnePlus’ Warp Charge, and Samsung’s Adaptive Fast Charging are a few examples of fast charging technology.
The topic at hand is: Would quick charging harm your phone’s battery? Just “no” is the response. Your smartphone phone’s battery is not harmed by fast charging. In actuality, the majority of current smartphone batteries are built to support quick charging.
These batteries include cutting-edge technology that controls the charging process to avoid overcharging, overheating, and other potential problems.
How do Smartphone Batteries Work?
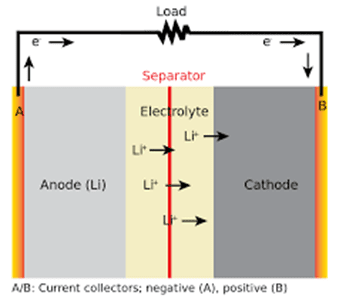
Lithium-ion batteries are often used in smartphones. These batteries feature a negative electrode (anode) made of graphite and a positive electrode (cathode) composed of lithium cobalt oxide. An electrolyte, a liquid or gel that conducts electricity, sits between the electrodes.
Lithium ions migrate from the cathode to the anode of a lithium-ion battery during charging, where they are stored in the graphite structure. Lithium ions flow through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode during discharge, creating the electrical current that powers the phone.
A smartphone’s battery management system (BMS) controls the battery’s charging and discharging processes and keeps track of the battery’s state of charge (SOC). The BMS also has safety measures to prevent the battery from being overcharged, overheated, or overdischarged, which might harm the battery or start a fire.
A lithium-ion battery’s capacity is expressed in milliampere-hours (mAh), which is the maximum amount of current it can deliver for an hour. The battery will last longer if the mAh rating is higher. The hardware, software, and usage habits of the phone, as well as other variables, also affect battery life.
Lithium-ion batteries, in general, have a short lifespan and will deteriorate over time, particularly if they are exposed to extreme heat or are kept at full charge for a lengthy period of time. It is crucial to take care of your phone’s battery by avoiding excessive temperatures and using the proper charger because this might result in a decrease in battery capacity and performance.
How Smartphone Batteries Drain Over the Period?
Source: DepositPhotos.com
Due to several circumstances, smartphone batteries frequently lose their charge over time. The following are some of the key causes of smartphone batteries depleting over time:
- Age: A smartphone battery tends to lose its ability to keep a charge more as it gets older. This is brought on by the battery’s natural aging process.
- Use patterns: Excessive use of the smartphone, such as using it for extended periods and running power-hungry apps, can quickly deplete the battery. Nonetheless, sparing use might make the battery last longer.
- Temperature: The battery may deplete more quickly in hotter climates. If you live in a hot region or use your smartphone in direct sunlight, this might be an issue.
- Habits of charging: Recurrently charging your smartphone battery to 100% or letting it discharge to 0% will reduce the life of the battery. When feasible, try to keep the battery charged between 20% and 80%.
- Software Updates: Updates to the software might occasionally result in a smartphone using more battery life than usual. This may be as a result of updated functionality or modifications to how the operating system consumes power.
- Background applications: Applications that operate in the background might use up battery life without your knowledge. To find out which applications are consuming the most power, it’s a good idea to often check the battery use settings on your device.
Therefore, if you want your smartphone battery to survive as long as possible, it’s critical to take proper care of it. This entails treating it with care, avoiding excessive temperatures, and paying attention to your charging routines.
Moreover, contemporary smartphones feature integrated charging controllers that stop the battery from getting more power than it can manage. This implies that your phone will limit the current to safeguard the battery even if you use a fast charger that provides greater power.
Fast charging does not permanently hurt your battery, but it might shorten its life. This is a crucial point to remember. The amount of charge cycles your battery can withstand may depend on the rate at which you charge your phone.
The number of times a battery may be charged and discharged before it begins to deteriorate is referred to as a charge cycle. Each battery can only be charged so many times before they are depleted.
Wrapping it All
In conclusion, quick charging won’t harm your phone’s battery, but it can shorten its life. Although the batteries in modern smartphones are made to support quick charging, frequent use can lower the battery’s capacity for charge cycles. Hence, in order to guarantee the longevity of your battery, it is crucial to utilize rapid charging infrequently and choose conventional charging techniques whenever feasible.






