Note: This is a guest post written by Jeeva Shanmugam – The development of self-driving cars has become a significant area of transportation technology in recent years.
With their cutting-edge sensors and artificial intelligence, these autonomous vehicles hope to revolutionize how we travel across space.
Self-driving cars promise improved road safety, decreased traffic, and more accessibility for people unable to drive conventional vehicles thanks to the seamless integration of robotics and driving.
This article examines the development of self-driving automobiles, charting their progression from conception to practical application while examining the revolutionary promise it has for the future of mobility.

Self-Driving Cars – Things You Should Know
The development of self-driving automobiles has taken unexpected turns as it has traveled through a difficult path of difficulties and successes.
However, the tides have changed recently, bringing us closer to a real future where driverless vehicles may soon become the norm.
This article explores the background of self-driving cars historically, the underlying technology driving their development, and the challenges that must be overcome before widespread use.
The History of Self-Driving Vehicles
Although the idea of autonomous vehicles has been around for millennia, substantial study into the technology didn’t begin until the 1960s. Ohio State University started working on a project to build self-driving automobiles in 1960.
These cars would use electrical devices on the road. Then, in 1966, General Motors developed a vehicle that a person could operate remotely.
However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that truly autonomous vehicles started to emerge. A van was converted into a self-driving vehicle called Navlab by Carnegie Mellon University in 1984. Navlab employed sensors and computers to traverse roadways.
Then, in 1987, a self-driving automobile capable of 60 mph was created by Mercedes-Benz and Bundeswehr University Munich.
The development carried on until the 1990s. NavLab 5 from Carnegie Mellon traveled 2,797 miles from Pittsburgh to San Diego by itself in 1995.
A research organization called DARPA also held the inaugural Grand Challenge in 1997, where teams raced to build self-driving cars that could complete a 132-mile desert course.
The DARPA Grand Challenge advanced research on self-driving automobiles significantly. Since then, there have been further trials and contests, greatly improving self-driving technology.
Technologies that Make Self-Driving Cars Possible
A variety of crucial technologies, each with a specific function, are necessary to enable self-driving automobiles.
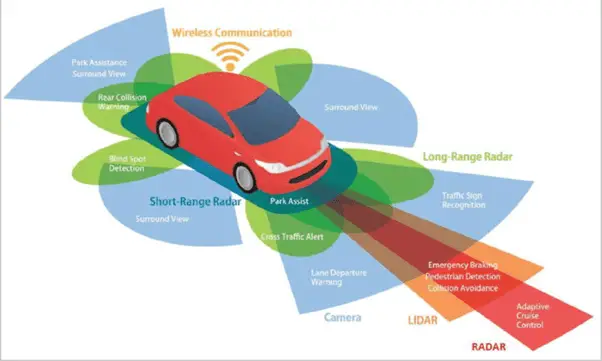
- Sensors: In order to interpret their environment, self-driving cars rely on a variety of sensors, including cameras, radar, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors. Cameras pick up on things like people and signs, radar picks up on far-off cars, lidar creates a 3D image of the surroundings, and ultrasonic sensors pick up on things like curbs that are close by.
- Computers: Self-driving cars’ potent computers, which interpret sensor data and make driving judgments, are the brains of these vehicles. These computers are used to recognize objects, anticipate their movements, and determine the safest and most effective paths.
- Software: Self-driving automobiles are controlled by sophisticated software. For a smooth driving experience, it gathers sensor data, makes driving decisions, and interacts with the car’s systems.
The Challenges of Self-Driving Cars
Before self-driving vehicles to become commonplace, a number of challenges still need to be cleared, despite the advancements that have been made. These difficulties include:

- Safety: It is one of the greatest problems self-driving cars are now experiencing. All types of driving situations, such as bad weather, congested traffic, and construction zones, must be handled properly by self-driving automobiles. Additionally, they must be capable of handling unforeseen situations like animals crossing the road or humans darting into the road.
- Regulation: It is another issue that self-driving cars must deal with. There is no international standard for self-driving automobiles, and each nation has its own set of laws. This makes it challenging for businesses to create and introduce self-driving vehicles on a worldwide level.
- Cost: The costs involved with creating and developing self-driving automobiles continue to be high. In underdeveloped countries, this cost barrier is particularly prominent and prevents widespread adoption.
- Public Trust: Gaining the public’s trust is a never-ending battle. Some people worry about their safety, while others are afraid of losing control of their automobiles.
The Future of Self-Driving Cars
The advent of self-driving automobiles has enormous potential to revolutionize transportation. These cutting-edge cars have the potential to improve traffic flow, reduce congestion, and encourage cleaner air. Additionally, they could provide a higher level of mobility for people who cannot drive, such as the elderly and those with impairments.
However, there are still several challenges to be solved before self-driving vehicles are a reality.
These difficulties include developing trustworthy sensors that can effectively sense their surroundings, creating safety-assuring real-time decision-making algorithms, and establishing suitable legal and regulatory standards for this new technology.
Despite these challenges, self-driving car technology is developing quickly, increasing the probability that we will see these autonomous cars on our roads in the near future.
Wrapping It All
In conclusion, the development of self-driving automobiles is evidence of human ingenuity and technological advancement. This path, from simple ideas to the sophisticated AI-powered cars we see today, illustrates our commitment to improving accessibility, efficiency, and road safety.
While there are still obstacles to overcome, advances in sensor technology, machine learning, and infrastructure integration open the door to a day when self-driving cars will transform transportation and alter how people view and use the roads.